Protein-coding gene in humans
| SCN3A |
|---|
 |
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | SCN3A, NAC3, Nav1.3, sodium voltage-gated channel alpha subunit 3, FFEVF4, EIEE62, DEE62 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 182391 MGI: 98249 HomoloGene: 56005 GeneCards: SCN3A |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 2 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 2q24.3 | Start | 165,087,526 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 165,204,050 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 2 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 2 C1.3|2 38.55 cM | Start | 65,287,462 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 65,397,971 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - endothelial cell
- middle temporal gyrus
- entorhinal cortex
- Brodmann area 23
- orbitofrontal cortex
- Region I of hippocampus proper
- postcentral gyrus
- Brodmann area 46
- cerebellar vermis
- superior frontal gyrus
|
| | Top expressed in | - superior cervical ganglion
- habenula
- dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus
- ventromedial nucleus
- piriform cortex
- paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus
- trigeminal ganglion
- ventral tegmental area
- temporal lobe
- supraoptic nucleus
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS |  | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - sodium channel activity
- voltage-gated ion channel activity
- ion channel activity
- voltage-gated sodium channel activity
| | Cellular component | - voltage-gated sodium channel complex
- cytoplasm
- integral component of membrane
- membrane
- plasma membrane
- axon
| | Biological process | - membrane depolarization during action potential
- sodium ion transmembrane transport
- sodium ion transport
- regulation of ion transmembrane transport
- ion transport
- transmembrane transport
- ion transmembrane transport
- neuronal action potential
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_001081676
NM_001081677
NM_006922 |
| NM_018732
NM_001355166
NM_001355167
NM_001355168
NM_001355169
|
|---|
NM_001355170
NM_001355171 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | |
|---|
NP_001075145
NP_001075146
NP_008853 |
| NP_001342095
NP_001342096
NP_001342097
NP_001342098
NP_001342099
|
|---|
NP_001342100
NP_061202 |
|
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 2: 165.09 – 165.2 Mb | Chr 2: 65.29 – 65.4 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|
Sodium channel, voltage-gated, type III, alpha subunit (SCN3A) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SCN3A gene.[5][6]
Function
Voltage-gated sodium channels are transmembrane glycoprotein complexes composed of a large alpha subunit with 24 transmembrane domains and one or more regulatory beta subunits. They are responsible for the generation and propagation of action potentials in neurons and muscle. This gene encodes one member of the sodium channel alpha subunit gene family, and is found in a cluster of five alpha subunit genes on chromosome 2. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[6]
SCN3A is involved in gyrification – the folding of the human cerebral cortex, and affects speech production brain areas.[7]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000153253 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000057182 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "UniProt". www.uniprot.org. Retrieved 24 July 2022.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: SCN3A sodium channel, voltage-gated, type III, alpha subunit".
- ^ Smith RS, Kenny CJ, Ganesh V, Jang A, Borges-Monroy R, Partlow JN, et al. (September 2018). "Sodium Channel SCN3A (NaV1.3) Regulation of Human Cerebral Cortical Folding and Oral Motor Development". Neuron. 99 (5): 905–913.e7. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2018.07.052. PMC 6226006. PMID 30146301.
Further reading
- Catterall WA, Goldin AL, Waxman SG (December 2005). "International Union of Pharmacology. XLVII. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated sodium channels". Pharmacological Reviews. 57 (4): 397–409. doi:10.1124/pr.57.4.4. PMID 16382098. S2CID 7332624.
- Malo MS, Srivastava K, Andresen JM, Chen XN, Korenberg JR, Ingram VM (April 1994). "Targeted gene walking by low stringency polymerase chain reaction: assignment of a putative human brain sodium channel gene (SCN3A) to chromosome 2q24-31". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 91 (8): 2975–9. Bibcode:1994PNAS...91.2975M. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.8.2975. PMC 43497. PMID 8159690.
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (September 1996). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery". Genome Research. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
- Lu CM, Brown GB (February 1998). "Isolation of a human-brain sodium-channel gene encoding two isoforms of the subtype III alpha-subunit". Journal of Molecular Neuroscience. 10 (1): 67–70. doi:10.1007/BF02737087. PMID 9589372. S2CID 2533542.
- Nagase T, Kikuno R, Ishikawa KI, Hirosawa M, Ohara O (February 2000). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XVI. The complete sequences of 150 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Research. 7 (1): 65–73. doi:10.1093/dnares/7.1.65. PMID 10718198.
- Gotthardt M, Trommsdorff M, Nevitt MF, Shelton J, Richardson JA, Stockinger W, Nimpf J, Herz J (August 2000). "Interactions of the low density lipoprotein receptor gene family with cytosolic adaptor and scaffold proteins suggest diverse biological functions in cellular communication and signal transduction". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 275 (33): 25616–24. doi:10.1074/jbc.M000955200. PMID 10827173.
- Chen YH, Dale TJ, Romanos MA, Whitaker WR, Xie XM, Clare JJ (December 2000). "Cloning, distribution and functional analysis of the type III sodium channel from human brain". The European Journal of Neuroscience. 12 (12): 4281–9. doi:10.1046/j.1460-9568.2000.01336.x. PMID 11122339.
- Kasai N, Fukushima K, Ueki Y, Prasad S, Nosakowski J, Sugata K, Sugata A, Nishizaki K, Meyer NC, Smith RJ (February 2001). "Genomic structures of SCN2A and SCN3A - candidate genes for deafness at the DFNA16 locus". Gene. 264 (1): 113–22. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(00)00594-1. PMID 11245985.
- Whitaker WR, Faull RL, Dragunow M, Mee EW, Emson PC, Clare JJ (2001). "Changes in the mRNAs encoding voltage-gated sodium channel types II and III in human epileptic hippocampus". Neuroscience. 106 (2): 275–85. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(01)00212-3. PMID 11566500. S2CID 26385238.
- Weiss LA, Escayg A, Kearney JA, Trudeau M, MacDonald BT, Mori M, Reichert J, Buxbaum JD, Meisler MH (February 2003). "Sodium channels SCN1A, SCN2A and SCN3A in familial autism". Molecular Psychiatry. 8 (2): 186–94. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001241. PMID 12610651. S2CID 16606651.
- Shah BS, Rush AM, Liu S, Tyrrell L, Black JA, Dib-Hajj SD, Waxman SG (August 2004). "Contactin associates with sodium channel Nav1.3 in native tissues and increases channel density at the cell surface". The Journal of Neuroscience. 24 (33): 7387–99. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0322-04.2004. PMC 6729770. PMID 15317864.
- Thimmapaya R, Neelands T, Niforatos W, Davis-Taber RA, Choi W, Putman CB, Kroeger PE, Packer J, Gopalakrishnan M, Faltynek CR, Surowy CS, Scott VE (July 2005). "Distribution and functional characterization of human Nav1.3 splice variants". The European Journal of Neuroscience. 22 (1): 1–9. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04155.x. PMID 16029190. S2CID 30185095.
- Platoshyn O, Remillard CV, Fantozzi I, Sison T, Yuan JX (November 2005). "Identification of functional voltage-gated Na(+) channels in cultured human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells". Pflügers Archiv. 451 (2): 380–387. doi:10.1007/s00424-005-1478-3. PMC 1351366. PMID 16052353.
- Kimura K, Wakamatsu A, Suzuki Y, Ota T, Nishikawa T, Yamashita R, Yamamoto J, Sekine M, Tsuritani K, Wakaguri H, Ishii S, Sugiyama T, Saito K, Isono Y, Irie R, Kushida N, Yoneyama T, Otsuka R, Kanda K, Yokoi T, Kondo H, Wagatsuma M, Murakawa K, Ishida S, Ishibashi T, Takahashi-Fujii A, Tanase T, Nagai K, Kikuchi H, Nakai K, Isogai T, Sugano S (January 2006). "Diversification of transcriptional modulation: large-scale identification and characterization of putative alternative promoters of human genes". Genome Research. 16 (1): 55–65. doi:10.1101/gr.4039406. PMC 1356129. PMID 16344560.
- Martin MS, Tang B, Ta N, Escayg A (August 2007). "Characterization of 5' untranslated regions of the voltage-gated sodium channels SCN1A, SCN2A, and SCN3A and identification of cis-conserved noncoding sequences". Genomics. 90 (2): 225–35. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2007.04.006. PMC 2637551. PMID 17544618.
External links
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
 | This membrane protein–related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |

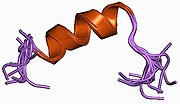 1byy: SODIUM CHANNEL IIA INACTIVATION GATE
1byy: SODIUM CHANNEL IIA INACTIVATION GATE
















