| RPS3 |
|---|
 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| List of PDB id codes |
|---|
1WH9, 4UG0, 4V6X, 5A2Q, 5AJ0, 3J7P, 4UJE, 4D5L, 3J7R, 4UJD, 4V5Z, 5FLX, 4D61, 4UJC |
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | RPS3, S3, ribosomal protein S3 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 600454; MGI: 1350917; HomoloGene: 779; GeneCards: RPS3; OMA:RPS3 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 11 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 11q13.4 | Start | 75,399,515 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 75,422,280 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 7 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 7 E1|7 54.07 cM | Start | 99,127,103 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 99,132,945 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - left ovary
- right ovary
- right uterine tube
- ventricular zone
- ganglionic eminence
- canal of the cervix
- epithelium of colon
- stromal cell of endometrium
- granulocyte
- body of uterus
|
| | Top expressed in | - otic vesicle
- epidermis
- tracheobronchial tree
- autopod region
- mesenteric lymph nodes
- hand
- ovary
- trachea
- ventricular zone
- lactiferous gland
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 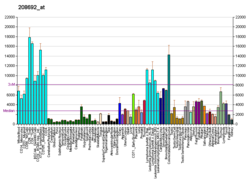
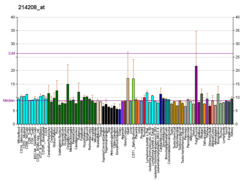 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - tubulin binding
- DNA N-glycosylase activity
- small ribosomal subunit rRNA binding
- iron-sulfur cluster binding
- transcription factor binding
- oxidized purine DNA binding
- Hsp70 protein binding
- lyase activity
- enzyme binding
- mRNA binding
- structural constituent of ribosome
- damaged DNA binding
- ubiquitin-like protein conjugating enzyme binding
- protein binding
- DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) endonuclease activity
- oxidized pyrimidine DNA binding
- endodeoxyribonuclease activity
- protein kinase binding
- supercoiled DNA binding
- DNA binding
- Hsp90 protein binding
- microtubule binding
- protein kinase A binding
- RNA binding
- kinase binding
- RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding
- protein-containing complex binding
- class I DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) endonuclease activity
- class III/IV DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) endonuclease activity
- oxidized purine nucleobase lesion DNA N-glycosylase activity
| | Cellular component | - cytoplasm
- cytosol
- polysome
- membrane
- focal adhesion
- ruffle membrane
- mitochondrion
- cytoskeleton
- nucleus
- ribosome
- nucleolus
- extracellular exosome
- plasma membrane
- spindle
- mitochondrial matrix
- small ribosomal subunit
- mitotic spindle
- mitochondrial inner membrane
- cytosolic small ribosomal subunit
- nucleoplasm
- extracellular matrix
- endoplasmic reticulum
- NF-kappaB complex
- postsynaptic density
- ribonucleoprotein complex
- synapse
| | Biological process | - chromosome segregation
- positive regulation of endodeoxyribonuclease activity
- cellular response to DNA damage stimulus
- positive regulation of microtubule polymerization
- cell cycle
- apoptotic process
- negative regulation of translation
- regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
- viral transcription
- response to TNF agonist
- positive regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway
- response to oxidative stress
- transcription, DNA-templated
- SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane
- positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in execution phase of apoptosis
- positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage
- positive regulation of DNA N-glycosylase activity
- positive regulation of JUN kinase activity
- nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, nonsense-mediated decay
- negative regulation of DNA repair
- positive regulation of DNA repair
- positive regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling
- cell division
- spindle assembly
- negative regulation of protein ubiquitination
- positive regulation of gene expression
- translational initiation
- regulation of translation
- cellular response to hydrogen peroxide
- protein biosynthesis
- positive regulation of base-excision repair
- DNA repair
- regulation of apoptotic process
- rRNA processing
- cytoplasmic translation
- positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly
- positive regulation of interleukin-2 production
- positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation
- positive regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway
- positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity
- cellular response to tumor necrosis factor
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_001260507
NM_001005
NM_001256802
NM_001260506 |
| |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | |
|---|
NP_000996
NP_001243731
NP_001247435
NP_001247436 |
| |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 11: 75.4 – 75.42 Mb | Chr 7: 99.13 – 99.13 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|

 1wh9: Solution structure of the KH domain of human ribosomal protein S3
1wh9: Solution structure of the KH domain of human ribosomal protein S3



















