Arkus tangens
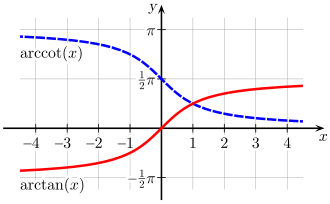
Arkus tangens je jedna z cyklometrických funkcí, inverzní funkce k funkci tangens. Obvykle se značí arctg x nebo arctan x, v anglické literatuře se taktéž používá atan x či tan−1 x. Její hodnotou je úhel v obloukové míře z intervalu , popřípadě ve stupňové míře z intervalu (−90°; 90°), jehož tangens je x. Je to jedna z nejdůležitějších funkcí matematické analýzy.
Definice
Funkce arctg x je inverzní funkce k funkci tg x, jejíž definiční obor byl omezen na interval . Díky tomuto omezení je výchozí funkce prostá, takže požadovaná inverzní funkce existuje.
Vlastnosti
Funkce v obloukové míře je bijekcí mezi množinou reálných čísel a intervalem , což mimo jiné dokazuje, že každý interval má stejnou mohutnost jako množina reálných čísel.
Dále má tato funkce následující vlastnosti:
| Definiční obor | |
|---|---|
| Obor hodnot | |
| Omezenost | Je omezená |
| Monotonie | Je rostoucí, a tedy prostá |
| Symetrie | Je lichá |
| Periodicita | Není periodická |
| Limity |
takže v okolí nuly je |
| Inverzní funkce | (tangens) |
| Derivace | |
| Integrál |
Vzorce
Poznámky
- ↑ Dosazením x = y do vzorce pro arctg x + arctg y
Externí odkazy
 Obrázky, zvuky či videa k tématu arkus tangens na Wikimedia Commons
Obrázky, zvuky či videa k tématu arkus tangens na Wikimedia Commons
| Goniometrické a související funkce | |
|---|---|
| Goniometrické funkce |
|
| Cyklometrické funkce | |
| Hyperbolické funkce | |
| Hyperbolometrické funkce | |


























