| PRKCB |
|---|
 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | PRKCB, PKC-beta, PKCB, PRKCB1, PRKCB2, protein kinase C beta, PKCbeta, PKCI(2) |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 176970; MGI: 97596; HomoloGene: 56424; GeneCards: PRKCB; OMA:PRKCB - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 16 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 16p12.2-p12.1 | Start | 23,835,983 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 24,220,611 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 7 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 7 F2|7 65.75 cM | Start | 121,887,974 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 122,233,625 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - middle temporal gyrus
- orbitofrontal cortex
- frontal pole
- Brodmann area 23
- Brodmann area 46
- superior frontal gyrus
- Brodmann area 10
- parietal lobe
- Region I of hippocampus proper
- postcentral gyrus
|
| | Top expressed in | - olfactory tubercle
- primary motor cortex
- Region I of hippocampus proper
- cingulate gyrus
- superior frontal gyrus
- visual cortex
- prefrontal cortex
- nucleus accumbens
- entorhinal cortex
- globus pallidus
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | |
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - transferase activity
- nucleotide binding
- protein kinase activity
- protein kinase C activity
- histone binding
- zinc ion binding
- calcium channel regulator activity
- chromatin binding
- metal ion binding
- kinase activity
- protein serine/threonine kinase activity
- protein binding
- androgen receptor binding
- nuclear receptor coactivator activity
- histone kinase activity (H3-T6 specific)
- ATP binding
- protein kinase C binding
- calcium-dependent protein kinase C activity
| | Cellular component | - cytoplasm
- membrane
- plasma membrane
- extracellular exosome
- nucleus
- nucleoplasm
- cytosol
- calyx of Held
- presynaptic cytosol
| | Biological process | - B cell receptor signaling pathway
- cellular response to carbohydrate stimulus
- positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway
- positive regulation of B cell receptor signaling pathway
- intracellular signal transduction
- response to hypoxia
- regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
- adaptive immune response
- phosphorylation
- immune system process
- regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- cellular calcium ion homeostasis
- transcription, DNA-templated
- positive regulation of angiogenesis
- platelet activation
- protein phosphorylation
- B cell activation
- negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway
- mitotic nuclear membrane disassembly
- negative regulation of glucose transmembrane transport
- positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity
- peptidyl-serine phosphorylation
- positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling
- calcium ion transport
- signal transduction
- lipoprotein transport
- apoptotic process
- regulation of myeloid cell differentiation
- chromatin organization
- presynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission
- positive regulation of nucleic acid-templated transcription
- regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|

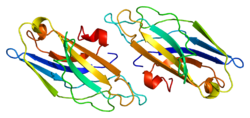
 1a25: C2 DOMAIN FROM PROTEIN KINASE C (BETA)
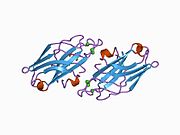
1a25: C2 DOMAIN FROM PROTEIN KINASE C (BETA) 2i0e: Structure of catalytic domain of human protein kinase C beta II complexed with a bisindolylmaleimide inhibitor
2i0e: Structure of catalytic domain of human protein kinase C beta II complexed with a bisindolylmaleimide inhibitor