Carboxypenicillin
Drug class


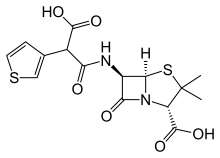
The carboxypenicillins are a group of antibiotics. They belong to the penicillin family and comprise the members carbenicillin and ticarcillin.[1]
Chemical structure
The carboxypenicillins feature the beta-lactam backbone of all penicillins but also feature a carboxylic acid or carboxylic acid ester group in the variable side-chain.[citation needed]
Spectrum
The carboxypenicillins exhibit activity against Gram negative organisms including Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Proteus species. They are inactive against certain Gram positive pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecalis, and L. monocytogenes. The carboxypenicillins are beta-lactamase sensitive.[citation needed]
See also
- Aminopenicillin
- Temocillin
References
- ^ "Mayo Clinic Proceedings". Retrieved 2015-12-08.
- v
- t
- e








