Calcium nitride
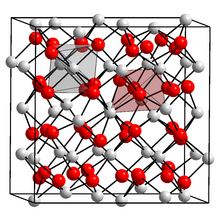 Unit cell containing 31 nitride ions (red) and 48 calcium ions (white). Each nitride is surrounded by six calcium, and each calcium by four nitride ions. | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Calcium nitride | |
| Other names tricalcium dinitride | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.435 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | Ca3N2 |
| Molar mass | 148.248 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | red-brown crystalline solid |
| Density | 2.670 g/cm3 2.63 g/cm3 (17 °C) |
| Melting point | 1,195 °C (2,183 °F; 1,468 K) |
Solubility in water | decomposes |
| Structure | |
Crystal structure | Cubic, cI80 |
Space group | Ia-3, No. 206 |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations | Beryllium nitride Magnesium nitride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).  Y verify (what is Y verify (what is  Y Y N ?) N ?) Infobox references | |
Calcium nitride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca3N2.[1] It exists in various forms (isomorphs), α-calcium nitride being more commonly encountered.
Structure
α-Calcium nitride adopts an anti-bixbyite structure, similar to Mn2O3, except that the positions of the ions are reversed: calcium (Ca2+) take the oxide (O2−) positions and nitride ions (N3−) the manganese (Mn3+). In this structure, Ca2+ occupies tetrahedral sites, and the nitride centres occupy two different types of octahedral sites.[2]
Synthesis and reactions
Calcium nitride is formed along with the oxide, CaO, when calcium burns in air. It can be produced by direct reaction of the elements:[3]
- 3 Ca + N2 → Ca3N2
It reacts with water or even the moisture in air to give ammonia and calcium hydroxide:[4]
- Ca3N2 + 6 H2O → 3 Ca(OH)2 + 2 NH3
Like sodium oxide, calcium nitride absorbs hydrogen above 350 °C:
- Ca3N2 + 2 H2 → 2 CaNH + CaH2
General references
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
References
- ^ Eagleson, M. (1994). Concise Encyclopedia Chemistry. Walter de Gruyter. p. 160. ISBN 3-11-011451-8.
Calcium nitride.
- ^ Wells, A.F. (1984) Structural Inorganic Chemistry, Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-855370-6.
- ^ P. Ehrlich “Calcium, Strontium, Barium Nitrides Ca3N2, Sr3N2, Ba3N2” in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed. Edited by G. Brauer, Academic Press, 1963, NY. Vol. 1. p. 940-1.
- ^ Heyns, A. (1998). "The Vibrational Spectra and Decomposition of α-Calcium Nitride (α-Ca3N2) and Magnesium Nitride (Mg3N2)". Journal of Solid State Chemistry. 137 (1): 33–41. Bibcode:1998JSSCh.137...33H. doi:10.1006/jssc.1997.7672.
External links
- WebElements entry
- v
- t
- e
- CaH2
- CaF2
- CaCl2
- Ca(ClO)2
- Ca(ClO3)2
- Ca(ClO4)2
- CaBr2
- Ca(BrO3)2
- CaI2
- Ca(IO3)2
- CaICl
- CaC2
- Ca(CN)2
- CaCN2
- CaCO3
- Ca(HCO3)2
- CaSi
- CaSi2
- Ca2SiO4
- Ca3(BO3)2
- CaAl2O4
- Ca3Al2O6
- Ca(MnO4)2
- CaCrO4
- CaTiO3
- CaC2O4
- Ca(HCO2)2
- Ca(CH3CO2)2
- Ca(C3H5O2)2
- CaC4H2O4
- Ca3(C6H5O7)2
- C3H7CaO6P
- Ca(C6H5O5S)2
- Ca(C6H7O6)2
- C10H11CaN4O8P
- CaC10H12O4N5PO4
- C10H16CaN2O8
- C12H22CaO14
- C14H26CaO16
- C18H32CaO19
- C36H70CaO4
- C24H40B2CaO24











