P53
| TP53 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 식별자 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 다른 이름 | TP53, BCC7, LFS1, P53, TRP53, tumor protein p53, BMFS5, Genes, p53 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 외부 ID | OMIM: 191170 MGI: 98834 HomoloGene: 460 GeneCards: TP53 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 위키데이터 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
p53은 암 억제 단백질로 인간은 TP53 유전자로 암호화되어 있다. P53은 다세포 생물의 세포 주기에서 암 억제자로서 암을 예방하기에 중요하다. 게놈의 돌연변이를 예방하여 게놈의 안정성을 보존하는 역할을 하기에 p53은 “게놈의 수호자”라고 서술된다.
p53의 이름은 분자량에서 온 것이다. SDS-PAGE에서 53,000 달톤 정도의 분자량을 보여준다. 그러나 아미노산 잔기들을 기초로 하여 계산해보면 p53의 질량은 단지 43,700 달톤 정도밖에 나오지 않는다. 이 차이는 단백질에 많은 수의 프롤린 잔기 때문인데, 이 때문에 SDS-PAGE에서 느린 진행 때문에 실제의 질량보다 더 무겁게 나온다. 이 현상은 사람, 설치류, 개구리, 그리고 어류를 포함하여 다양한 종류에서 관찰된다.
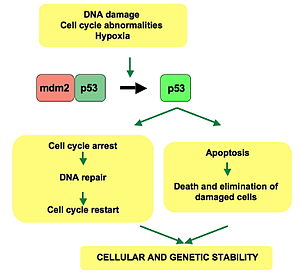
[5]G1기가 끝날 무렵, p53유전자에 의해 생성된 단백질은 세포의 DNA가 손상을 입었는지 점검한다. DNA가 건강하다면 p53은 세포분열을 진행시키고, 손상된 DNA를 발견할 경우에는 DNA를 활성화시켜 수선하기위한 다른 단백질을 유도한다. 만약 손상이 수선하기에 너무 치명적이면 p53단백질은 세포가 스스로 파괴되도록 유도한다. 이를 세포사멸(apoptosis)라고 부른다. 세포사멸은 변이된 세포가 계속 성장하지 못하도록한다. 다른 건강한 세포는 손상된 세포를 대체하기 위해 세포분열을 촉진한다.
만약 p53유전자의 돌연변이에 의해 p53단백질이 정상적으로 작동되지 못한다면 손상을 입은 DNA를 가진 세포는 세포분열을 진행할 수 있게 된다. 이러한 손상된 세포가 계속 분열을 할수록 손상된 DNA를 감지할 능력이 없으므로 더 많은 돌연변이를 낳게 된다. 이와 같은 돌연변이는 암을 유발한다.
유전좌위
사람의 p53유전자는 17번염색체 단완 (17p13.1)에 존재한다.
기능
p53 은 많은 항암 작용 메커니즘을 가지고 있으며, 세포자살, 유전체 안정성의 역할을 하며 혈관신생을 막는다. 항암작용으로 p53은 몇 가지 메커니즘을 거친다.
- DNA가 손상을 입었을 때, DNA수선 단백질을 활성화시킨다.
- 세포주기를 G1/S에서 멈추게 하여 성장을 막는다.
- DNA의 손상이 복구가 불가능하면 세포자살을 시작할 수 있다.
활성화된 p53은 DNA를 붙잡고 miR-34a mircoRNA를 포함한 몇몇의 유전자들을 발현시킨다.[6] WAF1/CIP1는 p21을 암호화 하고 있다. p21(WAF1)는 G1-S/CDK와 S/CDK복합체를 붙잡고 있다.
p21(WAF1)이 CDK2와 합쳐지게 되면 세포는 다음 분열단계로 진행할 수 없다. 돌연변이 p53은 효율적으로 DNA를 붙잡을 수 없기에 결국 "정지 신호"로써 작용할 수 없다.[7] 인간 배아 줄기 세포(human embryonic stem cells (hESCs)) 연구에서는 세포주기 제한과 DNA손상반응(DNA damage response)의 기능이 없는 p53-p21축을 공통적으로 서술하고 있다. 중요한점은, p21 mRNA는 명백하게 존재하며 hESCs의 DDR이후 상향 조절된다는 점이다.이 세포유형에서, p53은 다양한 mircoRNAs(miR-302a, miR-302b, miR-302c, miR-302d)를 활성화 시키며, 직접적으로 hESCs에서의 p21발현을 막는다.[8]
최근의 연구는 p53과 망막아세포종 단백질(Retinoblastoma protein, RB1) 경로를 연결하였다.[9]
백혈병 억제 인자(leukemia inhibitory factor, LIF)를 조절하는 p53은 쥐 모델에서 이식을 용이하게 해줌을 보여주었으며 인간에게도 가능하다는 것을 선사하였다.[10]
p53 발현은 DNA의 손상을 일으키는 자외선에 의해서 자극 될 수 있다. 이 경우에 p53은 태양에 피부를 그을리는 선탠에 의해 시작된다.[11][12]
period2
생체시계의 주요 유전자인 period와 관련된 period2 단백질의 양이 세포질과 세포핵내에서 p53의 양조절과 관련있다는 메커니즘을 KAIST의 김재경 수리과학과팀과 미국버지니아 공대와 공동으로 2016년 11월9일자 미국국립과학원회보(PNAS)에 발표한바있다.[13]

같이 보기
각주
- ↑ 가 나 다 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000141510 - 앙상블, May 2017
- ↑ 가 나 다 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000059552 - 앙상블, May 2017
- ↑ “Human PubMed Reference:”. 《National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine》.
- ↑ “Mouse PubMed Reference:”. 《National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine》.
- ↑ 생명과학개론 9판, Eldon D. Enger
- ↑ Mraz M, Malinova K, Kotaskova J, Pavlova S, Tichy B, Malcikova J, Stano Kozubik K, Smardova J, Brychtova Y (2009). “MiR-34a, miR-29c and miR-17-5p are downregulated in CLL patients with TP53 abnormalities”. 《Leukemia : official journal of the Leukemia Society of America, Leukemia Research Fund, U.K》 23 (6): 1159–63. doi:10.1038/leu.2008.377. PMID 19158830. CS1 관리 - 여러 이름 (링크)
- ↑ National Center for Biotechnology Information. “The p53 tumor suppressor protein”. 《Genes and Disease》. United States National Institutes of Health. 2008년 5월 28일에 확인함.
- ↑ Dolezalova D, Mraz M, Barta T, Plevova K, Vinarsky V, Holubcova Z, Jaros J, Dvorak P, Pospisilova S, Hampl A. (2012). “MicroRNAs regulate p21(Waf1/Cip1) protein expression and the DNA damage response in human embryonic stem cells.”. 《Stem Cells》 7: 1362–72. doi:10.1002/stem.1108.
|doi=값 확인 필요 (도움말). PMID 22511267. CS1 관리 - 여러 이름 (링크) - ↑ Bates S, Phillips AC, Clark PA, Stott F, Peters G, Ludwig RL, Vousden KH (1998). “p14ARF links the tumour suppressors RB and p53”. 《Nature》 395 (6698): 124–5. doi:10.1038/25867. PMID 9744267. CS1 관리 - 여러 이름 (링크)
- ↑ Hu W, Feng Z, Teresky AK, Levine AJ (2007년 11월). “p53 regulates maternal reproduction through LIF”. 《Nature》 450 (7170): 721–4. doi:10.1038/nature05993. PMID 18046411. 더 이상 지원되지 않는 변수를 사용함 (도움말) CS1 관리 - 여러 이름 (링크)
- ↑ “Genome's guardian gets a tan started”. New Scientist. 2007년 3월 17일. 2007년 3월 29일에 확인함.
- ↑ Cui R, Widlund HR, Feige E, Lin JY, Wilensky DL, Igras VE, D'Orazio J, Fung CY, Schanbacher CF, Granter SR, Fisher DE (2007). “Central role of p53 in the suntan response and pathologic hyperpigmentation”. 《Cell》 128 (5): 853–64. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.12.045. PMID 17350573. CS1 관리 - 여러 이름 (링크)
- ↑ (동아사이언스-잠 못자면 암 발병률 높아지는 원인 밝혀졌다)https://dongascience.donga.com/news.php?idx=14676 Archived 2020년 6월 4일 - 웨이백 머신