トレス海峡諸島民
| 総人口 | |
|---|---|
| 48,000 | |
| 居住地域 | |
| トレス海峡地域 (バマガ(Bamaga)、 セイシャ(Seisia)) | 6,000人 |
| クイーンズランド北部 (タウンズヴィル、ケアンズなど) | 42,000人[1] |
| 言語 | |
| トレス海峡島語(Torres Strait Island languages) | |
| 関連する民族 | |
| アボリジニ、パプアニューギニア人、メラネシア人 | |
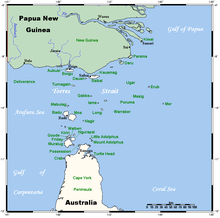

トレス海峡諸島民(トレスかいきょうしょとうみん、Torres Strait Islanders)は、オーストラリア・クイーンズランド州トレス海峡諸島の先住民。トレス海峡自治政府(詳細はトレス海峡諸島の項目を参照)を樹立している。
概要
- 文化的、生物的にメラネシア人、パプアニューギニア人と関連。アボリジニとは区別される。
- トレス海峡諸島民は、2型糖尿病の高い有病率を持つ[2]。2006年、成人人口の1/4が糖尿病2型を所持[3]
- 2017年にアボリジニ指導者らが憲法で定められている先住民の代表機関設置を求める心からのウルル声明(英語版)と題した嘆願書を作成したことをきっかけに、2023年10月14日にはトレス海峡諸島民とアボリジニを先住民と認め、議会や政府に意見を表明できる代表機関の設置を憲法に盛り込むことの是非を問う国民投票が執行されたが、代表機関の設置が先住民、非先住民ともに賛否両論となり結果的に憲法改正は否決された。ただし先住民と認めることに対しては改憲賛成派も反対派も特に異論はなかったとされる[4][5]。
言語
トレス海峡諸島語(Torres Strait Island languages)
- 西中部トレス海峡語(Western-central Torres Strait Language)
- 東部トレス海峡語(メリアム語、Meriam language)[6]
- 使用地域:東部
- パプア諸語のうち東トランスフライ語族(英語版)に分類される。
- トレス海峡諸島クレオール(英語版)
関連項目
参照
- ^ “Australia's Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples”. Australia Now. オーストラリア政府(Australian Government) 外務貿易省 (Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade). 2006年10月8日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2006年12月10日閲覧。
- ^ Antony G Faa & Peter J Holt (2002年7月10日). “Melioidosis in the Torres Strait Islands of Far North Queensland”. Commonwealth of Australia. 2011年7月4日閲覧。
- ^ “Diabetes epidemic”. Torres News. (2006年11月27日). http://www.torresnews.com.au/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=307%3Adiabetes-epidemic&catid=3%3Anews&Itemid=59 2011年7月4日閲覧。
- ^ “豪先住民、改憲巡り3極化=主流は賛成、左右に反対論”. 時事通信社. (2023年9月23日). https://sp.m.jiji.com/article/show/3054693 2023年10月15日閲覧。
- ^ “オーストラリア改憲案、国民的支持広がらず ヨーロッパ人侵略の歴史に「贖罪」の色濃く”. 日豪プレス. (2023年10月14日). https://nichigopress.jp/news-item/81171/ 2023年10月15日閲覧。
- ^ “Torres Strait Islanders”. Fact Sheets. オーストラリア政府(Australian Government)家族・共同体サービス・先住民事項庁 (Department of Families, Community Services and Indigenous Affairs). 2006年5月18日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2006年12月10日閲覧。
- ^ Torres Strait string figure example.
- ^ アルフレッド・コート・ハッドン(Haddon, Alfred Cort), along with one of his daughters, the pioneers in the modern study of Torres Strait string figures.
- ^ A string figure bibliography including examples from Torres Strait.
- ^ A popular and comprehensive book on string figures.
文献
- Davis, Richard (ed.) (2004). Woven Histories, Dancing Lives: Torres Strait Islander Identity, Culture and History. Aboriginal Studies Press, Canberra. ISBN 085575432X.
- Herle, Anita; Rouse, Sandra (ed.) (1998). Cambridge and the Torres Strait: Centenary Essays on the 1898 Anthropological Expedition. University Press, Cambridge. ISBN 0521584612.
外部リンク
- Torres Strait Regional Authority
- Church of Torres Strait
- Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islanders' virtual books - クイーンズランド州立図書館
- Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Social Justice Commissioner, Social Justice Reports 1994-2009 and Native Title Reports 1994-2009 for more information about Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander affairs.
- アルフレッド・コート・ハッドン(Haddon, Alfred Cort) (1901年). Head-hunters; black, white, and brown.





