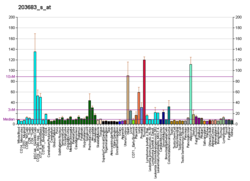
Vascular endothelial growth factor B
| VEGFB | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | VEGFB, VEGFL, VRF, vascular endothelial growth factor B | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 601398; MGI: 106199; HomoloGene: 87131; GeneCards: VEGFB; OMA:VEGFB - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vascular endothelial growth factor B also known as VEGF-B is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the VEGF-B gene.[5] VEGF-B is a growth factor that belongs to the vascular endothelial growth factor family, of which VEGF-A is the best-known member.
Function
In contrast to VEGF-A, VEGF-B plays a less pronounced role in the vascular system: Whereas VEGF-A is important for the formation of blood vessels, such as during development or in pathological conditions, VEGF-B seems to play a role only in the maintenance of newly formed blood vessels during pathological conditions.[6] VEGF-B plays also an important role on several types of neurons. It is important for the protection of neurons in the retina[7] and the cerebral cortex during stroke,[8] and of motor neurons during motor neuron diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.[9]
VEGF-B exerts its effects via the FLT1 receptor.[10] But the role of co-receptor NRP in VEGF-B-mediated effects is still unclear.[11]
VEGF-B has also been found to control endothelial uptake and transport of fatty acids in heart and skeletal muscle.[12][13]
Interactions
Vascular endothelial growth factor B has been shown to interact with FLT1, NRP1 and NRP2.[14][15][16][17]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000173511 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000024962 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: VEGFB vascular endothelial growth factor B".
- ^ Zhang F, Tang Z, Hou X, Lennartsson J, Li Y, Koch AW, et al. (April 2009). "VEGF-B is dispensable for blood vessel growth but critical for their survival, and VEGF-B targeting inhibits pathological angiogenesis". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 106 (15): 6152–6157. Bibcode:2009PNAS..106.6152Z. doi:10.1073/pnas.0813061106. PMC 2669337. PMID 19369214.
- ^ Li Y, Zhang F, Nagai N, Tang Z, Zhang S, Scotney P, et al. (March 2008). "VEGF-B inhibits apoptosis via VEGFR-1-mediated suppression of the expression of BH3-only protein genes in mice and rats". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 118 (3): 913–923. doi:10.1172/JCI33673. PMC 2230661. PMID 18259607.
- ^ Sun Y, Jin K, Childs JT, Xie L, Mao XO, Greenberg DA (October 2004). "Increased severity of cerebral ischemic injury in vascular endothelial growth factor-B-deficient mice". Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. 24 (10): 1146–1152. doi:10.1097/01.wcb.0000134477.38980.38. PMID 15529014.
- ^ Poesen K, Lambrechts D, Van Damme P, Dhondt J, Bender F, Frank N, et al. (October 2008). "Novel role for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor-1 and its ligand VEGF-B in motor neuron degeneration". The Journal of Neuroscience. 28 (42): 10451–10459. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1092-08.2008. PMC 6671326. PMID 18923022.
- ^ Yamazaki Y, Morita T (November 2006). "Molecular and functional diversity of vascular endothelial growth factors". Molecular Diversity. 10 (4): 515–527. doi:10.1007/s11030-006-9027-3. PMID 16972015. S2CID 28692204.
- ^ Mallick R, Ylä-Herttuala S (December 2022). "Therapeutic Potential of VEGF-B in Coronary Heart Disease and Heart Failure: Dream or Vision?". Cells. 11 (24): 4134. doi:10.3390/cells11244134. PMC 9776740. PMID 36552897.
- ^ Muoio DM (July 2010). "Metabolism and vascular fatty acid transport". The New England Journal of Medicine. 363 (3): 291–293. doi:10.1056/NEJMcibr1005397. PMID 20647206.
- ^ Hagberg CE, Mehlem A, Falkevall A, Muhl L, Fam BC, Ortsäter H, et al. (October 2012). "Targeting VEGF-B as a novel treatment for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes". Nature. 490 (7420): 426–430. Bibcode:2012Natur.490..426H. doi:10.1038/nature11464. PMID 23023133. S2CID 4315297.
- ^ Olofsson B, Korpelainen E, Pepper MS, Mandriota SJ, Aase K, Kumar V, et al. (September 1998). "Vascular endothelial growth factor B (VEGF-B) binds to VEGF receptor-1 and regulates plasminogen activator activity in endothelial cells". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 95 (20): 11709–11714. Bibcode:1998PNAS...9511709O. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.20.11709. PMC 21705. PMID 9751730.
- ^ Makinen T, Olofsson B, Karpanen T, Hellman U, Soker S, Klagsbrun M, et al. (July 1999). "Differential binding of vascular endothelial growth factor B splice and proteolytic isoforms to neuropilin-1". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 274 (30): 21217–21222. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.30.21217. PMID 10409677.
- ^ Mallick R, Ylä-Herttuala S (December 2022). "Therapeutic Potential of VEGF-B in Coronary Heart Disease and Heart Failure: Dream or Vision?". Cells. 11 (24): 4134. doi:10.3390/cells11244134. PMC 9776740. PMID 36552897.
- ^ Mallick R, Gurzeler E, Toivanen PI, Nieminen T, Ylä-Herttuala S (2022-08-04). "Novel Designed Proteolytically Resistant VEGF-B186R127S Promotes Angiogenesis in Mouse Heart by Recruiting Endothelial Progenitor Cells". Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology. 10: 907538. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2022.907538. PMC 9385986. PMID 35992336.
Further reading
- Poesen K, Lambrechts D, Van Damme P, Dhondt J, Bender F, Frank N, et al. (October 2008). "Novel role for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor-1 and its ligand VEGF-B in motor neuron degeneration". The Journal of Neuroscience. 28 (42): 10451–10459. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1092-08.2008. PMC 6671326. PMID 18923022.
- Joukov V, Kaipainen A, Jeltsch M, Pajusola K, Olofsson B, Kumar V, et al. (November 1997). "Vascular endothelial growth factors VEGF-B and VEGF-C". Journal of Cellular Physiology. 173 (2): 211–215. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199711)173:2<211::AID-JCP23>3.0.CO;2-H. PMID 9365524. S2CID 2930599.
- Olofsson B, Pajusola K, Kaipainen A, von Euler G, Joukov V, Saksela O, et al. (March 1996). "Vascular endothelial growth factor B, a novel growth factor for endothelial cells". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 93 (6): 2576–2581. Bibcode:1996PNAS...93.2576O. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.6.2576. PMC 39839. PMID 8637916.
- Olofsson B, Pajusola K, von Euler G, Chilov D, Alitalo K, Eriksson U (August 1996). "Genomic organization of the mouse and human genes for vascular endothelial growth factor B (VEGF-B) and characterization of a second splice isoform". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 271 (32): 19310–19317. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.32.19310. PMID 8702615.
- Grimmond S, Lagercrantz J, Drinkwater C, Silins G, Townson S, Pollock P, et al. (February 1996). "Cloning and characterization of a novel human gene related to vascular endothelial growth factor". Genome Research. 6 (2): 124–131. doi:10.1101/gr.6.2.124. PMID 8919691.
- Olofsson B, Korpelainen E, Pepper MS, Mandriota SJ, Aase K, Kumar V, et al. (September 1998). "Vascular endothelial growth factor B (VEGF-B) binds to VEGF receptor-1 and regulates plasminogen activator activity in endothelial cells". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 95 (20): 11709–11714. Bibcode:1998PNAS...9511709O. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.20.11709. PMC 21705. PMID 9751730.
- Makinen T, Olofsson B, Karpanen T, Hellman U, Soker S, Klagsbrun M, et al. (July 1999). "Differential binding of vascular endothelial growth factor B splice and proteolytic isoforms to neuropilin-1". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 274 (30): 21217–21222. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.30.21217. PMID 10409677.
- Ikuta T, Ariga H, Matsumoto K (November 2000). "Extracellular matrix tenascin-X in combination with vascular endothelial growth factor B enhances endothelial cell proliferation". Genes to Cells. 5 (11): 913–927. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2443.2000.00376.x. PMID 11122379. S2CID 41366972.
- Qi JH, Ebrahem Q, Moore N, Murphy G, Claesson-Welsh L, Bond M, et al. (April 2003). "A novel function for tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 (TIMP3): inhibition of angiogenesis by blockage of VEGF binding to VEGF receptor-2". Nature Medicine. 9 (4): 407–415. doi:10.1038/nm846. PMID 12652295. S2CID 12563403.
- Trompezinski S, Berthier-Vergnes O, Denis A, Schmitt D, Viac J (February 2004). "Comparative expression of vascular endothelial growth factor family members, VEGF-B, -C and -D, by normal human keratinocytes and fibroblasts". Experimental Dermatology. 13 (2): 98–105. doi:10.1111/j.0906-6705.2004.00137.x. PMID 15009103. S2CID 13040175.
- Timoshenko AV, Chakraborty C, Wagner GF, Lala PK (April 2006). "COX-2-mediated stimulation of the lymphangiogenic factor VEGF-C in human breast cancer". British Journal of Cancer. 94 (8): 1154–1163. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6603067. PMC 2361247. PMID 16570043.
- Iyer S, Scotney PD, Nash AD, Ravi Acharya K (May 2006). "Crystal structure of human vascular endothelial growth factor-B: identification of amino acids important for receptor binding". Journal of Molecular Biology. 359 (1): 76–85. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.03.002. PMID 16616187.
- Yamada E, Yamazaki K, Takano K, Obara T, Sato K (June 2006). "Iodide inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor-A expression in cultured human thyroid follicles: a microarray search for effects of thyrotropin and iodide on angiogenesis factors". Thyroid. 16 (6): 545–554. doi:10.1089/thy.2006.16.545. PMID 16839256.
- de Paulis A, Prevete N, Fiorentino I, Rossi FW, Staibano S, Montuori N, et al. (November 2006). "Expression and functions of the vascular endothelial growth factors and their receptors in human basophils". Journal of Immunology. 177 (10): 7322–7331. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.177.10.7322. PMID 17082651.
External links
- PDBe-KB provides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Human Vascular endothelial growth factor B
- v
- t
- e
-
 2c7w: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN VASCULAR ENDOTHELIAL GROWTH FACTOR-B: IDENTIFICATION OF AMINO ACIDS IMPORTANT FOR ANGIOGENINC ACTIVITY
2c7w: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN VASCULAR ENDOTHELIAL GROWTH FACTOR-B: IDENTIFICATION OF AMINO ACIDS IMPORTANT FOR ANGIOGENINC ACTIVITY