Inferior epigastric artery
| Inferior epigastric artery | |
|---|---|
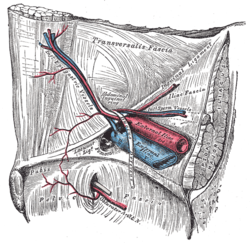 Right inferior epigastric artery - view from inside of abdomen. (Inferior epigastric vessels labeled at upper left.) | |
 The abdominal inguinal ring. (Inf. epigastric artery labeled at center left.) | |
| Details | |
| Source | External iliac artery |
| Branches | Cremasteric artery, pubic branch of inferior epigastric artery, artery of round ligament of uterus ♀ |
| Vein | Inferior epigastric vein |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria epigastrica inferior |
| TA98 | A12.2.16.003 |
| TA2 | 4358 |
| FMA | 20686 |
| Anatomical terminology [edit on Wikidata] | |
In human anatomy, the inferior epigastric artery is an artery that arises from the external iliac artery.[1]: 225 It is accompanied by the inferior epigastric vein; inferiorly, these two inferior epigastric vessels together travel within the lateral umbilical fold (which represents the lateral border of Hesselbach's triangle, the area through which direct inguinal hernias protrude.[2]) The inferior epigastric artery then traverses the arcuate line of rectus sheath to enter the rectus sheath,[1]: 234 then anastomoses with the superior epigastric artery within the rectus sheath.[1]: 225
Structure
Origin
The inferior epigastric artery arises from the external iliac artery, immediately superior to the inguinal ligament.[3]
Course and relations
It curves forward in the subperitoneal tissue, and then ascends obliquely along the medial margin of the abdominal inguinal ring; continuing its course upward, it pierces the transversalis fascia, and, passing in front of the linea semicircularis, ascends between the rectus abdominis muscle and the posterior lamella of its sheath.
It finally divides into numerous branches, which anastomose, above the umbilicus, with the superior epigastric branch of the internal thoracic artery and with the lower intercostal arteries.
As the inferior epigastric artery passes obliquely upward from its origin it lies along the lower and medial margins of the abdominal inguinal ring, and behind the commencement of the spermatic cord.
The vas deferens, as it leaves the spermatic cord in the male, and the round ligament of the uterus in the female, winds around the lateral and posterior aspects of the artery.
Anastomoses
It anastomoses with the superior epigastric artery.[3]
Clinical significance
Hernia
The inferior epigastric artery may lie close to an inguinal hernia, so acts as a useful landmark.[4]
Surgery
The inferior epigastric artery may be damaged during laparoscopic surgery.[4] It may also be damaged when manually finding the peritoneum beneath the rectus abdominis muscle.[4]
Additional images
-
 The interfoveolar ligament, seen from in front.
The interfoveolar ligament, seen from in front. -
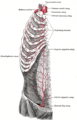 The internal mammary artery and its branches.
The internal mammary artery and its branches. -
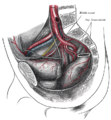 The arteries of the pelvis.
The arteries of the pelvis. -
 The iliac veins.
The iliac veins. -
 Dissection of side wall of pelvis showing sacral and pudendal plexuses.
Dissection of side wall of pelvis showing sacral and pudendal plexuses. -
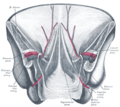 Posterior view of the anterior abdominal wall in its lower half. The peritoneum is in place, and the various cords are shining through.
Posterior view of the anterior abdominal wall in its lower half. The peritoneum is in place, and the various cords are shining through. -
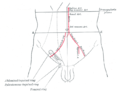 Front of abdomen, showing surface markings for arteries and inguinal canal.
Front of abdomen, showing surface markings for arteries and inguinal canal. -
 Schema of the arteries arising from the external iliac and femoral arteries.
Schema of the arteries arising from the external iliac and femoral arteries.
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 623 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 623 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ a b c Sinnatamby C (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
- ^ Wu WT, Chang KV, Lin CP, Yeh CC, Özçakar L (July 2022). "Ultrasound imaging for inguinal hernia: a pictorial review". Ultrasonography. 41 (3): 610–623. doi:10.14366/usg.21192. PMC 9262670. PMID 35569836.
- ^ a b Castro Ferreira M, Henrique Ishida L, Munhoz A (January 2009). "CHAPTER 19 - Rectus flap". In Wei FC, Mardini S (eds.). Flaps and Reconstructive Surgery. Edinburgh: W.B. Saunders. pp. 207–223. doi:10.1016/B978-0-7216-0519-7.00019-8. ISBN 978-0-7216-0519-7.
- ^ a b c Paterson-Brown S (January 2010). "Chapter Five - Applied anatomy". In Bennett P, Williamson C (eds.). Basic Science in Obstetrics and Gynaecology (Fourth ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 57–95. doi:10.1016/b978-0-443-10281-3.00009-9. ISBN 978-0-443-10281-3.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 35:04-07 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Incisions and the contents of the rectus sheath."
- Anatomy photo:35:12-0104 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Anterior Abdominal Wall: Blood Vessels in the Rectus sheath"
- Anatomy image:7282 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Anatomy image:7326 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Anatomy image:7542 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Anatomy image:7578 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- figures/chapter_25/25-9.HTM: Basic Human Anatomy at Dartmouth Medical School
- v
- t
- e
aorta
| Inferior phrenic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Celiac |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Superior mesenteric | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Suprarenal | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Renal | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gonadal | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lumbar | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inferior mesenteric | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common iliac |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Median sacral | |||||||||||||||||||||||||



















