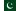Hispar Glacier

Hispar Glacier (Balti: ཧིསྤར་གངས།, romanized: Hispar gangs; Urdu: ہسپر گلیشر) is a 49-km (30-mile) long glacier situated in the Karakoram Mountains of Gilgit–Baltistan, Pakistan. It converges with the Biafo Glacier, which extends for 67 kilometers (42 miles), at the Hispar La (Pass), reaching an altitude of 5,128 meters (16,824 feet). This confluence creates the world's longest glacial system outside of the polar regions.
Details
The 100-km (62-mile) long ice highway serves as a connecting route between two ancient mountain kingdoms: Nagar in the west and Baltistan in the east. The upper half of Biafo is particularly challenging due to the steep terrain and strenuous boulder hopping required on the lateral moraines and hillsides. The traverse becomes especially demanding when crossing the four major tributary glaciers from the north, and potential high nullah (stream) crossings can be hazardous.[1]


Rivers
The Hispar River, a tributary of the Hunza River, rises from the meltwater of the glacier.
See also
- Central Karakoram National Park
- List of mountains in Pakistan
- List of highest mountains
- List of longest glaciers
- Hispar Muztagh
References
- ^ "Snow Lake Biafo Hispar Glacier Trek". Archived from the original on 2006-03-16. Retrieved 2006-04-21.
External links
- Northern Pakistan detailed placemarks in Google Earth
- v
- t
- e
- Abruzzi Glacier
- Baltoro Glacier
- Batura Glacier
- Biafo Glacier
- Biarchedi Glacier
- Chogo Lungma Glacier
- Chumik Glacier
- Godwin-Austen Glacier
- Gondogoro Glacier
- Hainablak Glacier
- Hispar Glacier
- Kutiah Lungma Glacier
- Miar Glacier
- Panmah Glacier
- Passu Glacier
- Rupal Glacier
- Shani Glacier
- Trango Glacier
- Vigne Glacier
 Pakistan portal
Pakistan portal Category
Category
 | This Gilgit-Baltistan location article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e
 | This Pakistan location article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e