Cadinenes
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
IUPAC names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
CAS Number |
| ||
| ChEBI |
| ||
| ChEMBL |
| ||
| KEGG |
| ||
PubChem CID |
| ||
| UNII |
| ||
| Properties | |||
Chemical formula | C15H24 | ||
| Molar mass | 204.357 g·mol−1 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).  Y verify (what is Y verify (what is  Y Y N ?) N ?) Infobox references | |||
Cadinenes are a group of isomeric hydrocarbons that occur in a wide variety of essential oil-producing plants. The name is derived from that of the Cade juniper (Juniperus oxycedrus L.), the wood of which yields an oil from which cadinene isomers were first isolated.
Chemically, the cadinenes are bicyclic sesquiterpenes. The term cadinene has sometimes also been used in a broad sense to refer to any sesquiterpene with the so-called cadalane (4-isopropyl-1,6-dimethyldecahydronaphthalene) carbon skeleton. Because of the large number of known double-bond and stereochemical isomers, this class of compounds has been subdivided into four subclasses based on the relative stereochemistry at the isopropyl group and the two bridgehead carbon atoms.[1] The name cadinene is now properly used only for the first subclass below, which includes the compounds originally isolated from cade oil. Only one enantiomer of each subclass is depicted, with the understanding that the other enantiomer bears the same subclass name.
-
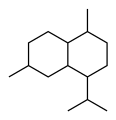 Cadalane skeleton
Cadalane skeleton -
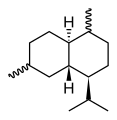 Cadinane stereochemistry
Cadinane stereochemistry -
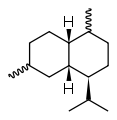 Muurolane stereochemistry
Muurolane stereochemistry -
 Amorphane stereochemistry
Amorphane stereochemistry -
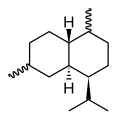 Bulgarane stereochemistry
Bulgarane stereochemistry
References
- ^ A.-K. Borg-Karlson, T. Norin and A. Talvitie (1981). "Configurations and conformations of torreyol (δ-cadinol), α-cadinol, T-muurolol and T-cadinol". Tetrahedron. 37 (2): 425–430. doi:10.1016/s0040-4020(01)92031-9.




















