African clawless otter
| African clawless otter | |
|---|---|
 | |
| On the banks of the Okavango River, Namibia | |
Conservation status | |
CITES Appendix II (CITES)[2] | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Mustelidae |
| Genus: | Aonyx Lesson, 1827 |
| Species: | A. capensis[1] |
| Binomial name | |
| Aonyx capensis[1] (Schinz, 1821) | |
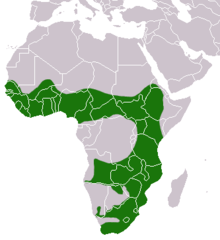 | |
| African clawless otter range | |
| Synonyms[3] | |
| |
The African clawless otter (Aonyx capensis), also known as the Cape clawless otter or groot otter, is the second-largest freshwater otter species. It inhabits permanent water bodies in savannah and lowland forest areas through most of sub-Saharan Africa.[2] It is characterised by partly webbed and clawless feet, from which their name is derived. The word 'aonyx' means clawless, derived from the prefix a- ("without") and onyx ("claw/hoof").
Taxonomy
Aonyx capensis is a member of the weasel family (Mustelidae) and of the order Carnivora. The earliest known species of otter, Potamotherium valetoni, occurred in the upper Oligocene of Europe: A. capensis first appears in the fossil record during the Pleistocene.[4] Aonyx is closely related to the extinct giant Sardinian otter, Megalenhydris.[citation needed]
Subspecies
Mammal Species of the World lists six subspecies of the African clawless otter:[1]
- A. c. capensis (Schinz, 1821)
- A. c. hindei (Thomas, 1905)
- A. c. meneleki (Thomas, 1903)
- A. c. microdon (Pohle, 1920)
- A. c. philippsi (Hinton, 1921)
Until recently the Congo clawless otter was considered a subspecies as well, but recent authorities treat it as a separate species A. congicus.[2][4]
Description

The African clawless otter has a chestnut-coloured thick, smooth fur with almost silky underbellies. It is characterized by white facial markings that extend downward towards its throat and chest areas. Paws are partially webbed with five fingers, but without opposable thumbs. All lack claws except for digits 2, 3, and 4 of the hind feet. Its large skull is broad and flat, with a relatively small orbit and a short snout. Molars are large and flat, used for crushing of prey. Male otters are slightly larger than females on average. Adults are 113–163 cm (44–64 in) in length, including their tails that comprised about a third of their length. Weights range from 10–36 kg (22–79 lb), with most otters averaging between 12 and 21 kg (26 and 46 lb). They are the third largest otter on average after the sea otter and giant otter and probably the third largest extant mustelid appearing to slightly outrival the wolverine, hog badger and European badger in mean body mass.[5][6] Despite being closely related to the Asian small-clawed otter, the African clawless otter is often twice as massive as that relatively diminutive mustelid.
Distribution and habitat
African clawless otters can be found anywhere from open coastal plains, to semiarid regions, to densely forested areas. Surviving mostly in southern Africa, the otters live in areas surrounding permanent bodies of water, usually surrounded by some form of foliage. Logs, branches, and loose foliage greatly appeal to the otter as this provides shelter, shade, and great rolling opportunities. Slow and rather clumsy on land, they build burrows in banks near water, allowing for easier food access and a quick escape from predators. In the False Bay area of the Cape Peninsula, they have been observed scavenging along beaches and rocks and hunting in shallow surf for mullet. They are mainly nocturnal in urban areas and lie up during the day in quiet, bushy areas.
Behaviour and ecology


Though mostly solitary animals, African clawless otters will live in neighboring territories of family groups of up to five individuals. Each still having its own range within that territory, they mostly keep to themselves unless seeking a mate. Territories are marked using a pair of anal glands which secrete a particular scent. Each otter is very territorial over its particular range.
The African clawless otter spends its days swimming and catching food. They return to burrows (holts) for safety, cooling or a rubdown using grasses and leaves. Mainly aquatic creatures, their tails are used for locomotion and propel them through the water. They are also used for balance when walking or sitting upright.
Reproduction
Females give birth to litters containing two to five young around early spring. Mating takes place in short periods throughout the rainy season in December. Afterwards, both males and females go their separate ways and return to their solitary lives once more. Young are raised solely by the females. Gestation lasts around two months (63 days). Weaning takes place between 45 and 60 days, with the young reaching full maturity around one year of age.
Diet
The diet of Aonyx capensis primarily includes water-dwelling animals, such as crabs, fish, frogs and worms. They dive after prey to catch it, then swim to shore again, where they eat. Their fore paws come in handy as searching devices and are great tools for digging on the muddy bottoms of ponds and rivers, picking up rocks and looking under logs. Extremely sensitive whiskers (vibrissae) are used as sensors in the water to pick up the movements of potential prey.
Predation
Quick in the water and burrowing on land, the African clawless otter does not have many predators. Its greatest threat comes from the python, which will often lie in wait near or in the water. Other predators would include the crocodile and African fish eagle. If threatened, a high-pitched scream is emitted to warn neighboring otters and confuse a predator.
Thermoregulation
Living in Africa, environments can become very hot. Staying cool means spending time in the water, and using burrows as a way to escape the highest temperatures of the day. To stay warm, on the other hand, the otters depend solely on their thick fur. Guard hairs cover the body, acting as insulation. Since the otter lacks an insulating layer of body fat, its only means of warmth is provided by its thick coat of fur.
Threats
The biggest threat to African clawless otters comes from humans. Aonyx specimens will often forage in man-made fisheries and may be hunted or become entangled in nets. Overfishing by humans may reduce the food supply available to otters. They are sometimes hunted for their thick, soft pelts, which humans use in forms of clothing. In forested areas, logging may be a major threat, since erosion leads to greatly increased turbidity in rivers which can in turn greatly reduce the populations of fish on which the otters depend. This may well be a far greater threat to otters than hunting. The Otter Trail is a hiking trail in South Africa named after the African clawless otter, which is found in this area. Otters along the trail are protected, as it falls within the Tsitsikamma National Park.
References
- ^ a b Wozencraft, W. C. (2005). "Aonyx capensis". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 532–628. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ a b c d Jacques, H.; Reed-Smith, J. & Somers, M.J. (2021). "Aonyx capensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2021: e.T1793A164575819. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-3.RLTS.T1793A164575819.en. Retrieved 12 December 2022.
- ^ "Oldstyle id: 577b8ce82b7857d1ada9c14614d1240a". Catalogue of Life. Species 2000: Leiden, the Netherlands.
- ^ a b Larivière, S. (2001). "Aonyx capensis" (PDF). Mammalian Species (671): 1–6. doi:10.1644/1545-1410(2001)671<0001:ac>2.0.co;2. S2CID 198968982.
- ^ African Clawless Otter. Archived 2011-08-30 at the Wayback Machine Arkive.org. 2011.
- ^ African Clawless Otter. The Animal Files. 2011.
Further reading
- Somers, M. J. & Nel, J. A. J. (2000). "Habitat selection by the Cape clawless otter (Aonyx capensis) in rivers in the Western Cape Province, South Africa". African Journal of Ecology. 42 (4): 298–305. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2028.2004.00526.x.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Somers, M. J. (2000). "Foraging behaviour of Cape clawless otters (Aonyx capensis) in a marine habitat". Journal of Zoology. 252 (4): 473–480. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.2000.tb01230.x.
External links
- Animal Diversity Web
- AmericaZoo
- Otternet
- Itech: African Clawless Otter
- v
- t
- e
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Infraclass: Eutheria
- Superorder: Laurasiatheria
Suborder Feliformia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Family Felidae | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||
Family Viverridae | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Family Eupleridae | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Suborder Caniformia (cont. below) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Suborder Caniformia (cont. above) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Family Mustelidae | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||











